Check Point's latest firewall innovation brings the industry's strongest URL Filtering, application and identity control to organizations of all sizes. You can easily create policies which detect or block thousands of applications and internet sites.
Use the Application Control and URL Filtering blades to:
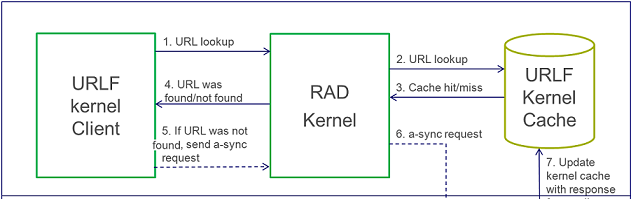
URL Filtering Categorization Flow
FeaturesFeature - HTTPS FilteringCategorization of HTTPS sites without HTTPS inspection (passive HTTPS). Supports URL Filtering on HTTPS traffic without HTTPS inspection.To enable it, enable the URL Filtering blade: Go to Application & URL Filtering tab -> Advanced -> Engine Settings -> Enable "Categorize HTTPS sites" and install Security policy How it works A cache table cptls_server_cn_cache is used here. The cache saves mapping between IP+Port to CN (certificate's Canonical Name) and a flag if the CN is valid. 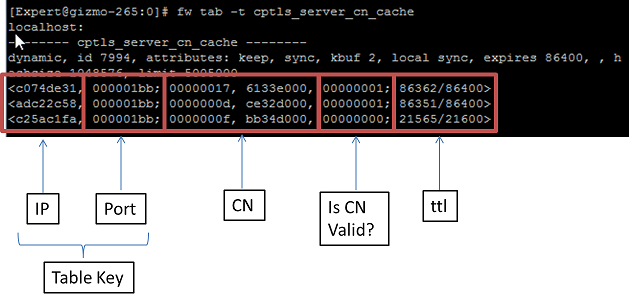 When SSL traffic is coming, the request (client hello) is recognized by PM (Pattern Matcher) matching on one of SSL request signatures internal procedure. Then the IP+Port will be extracted from the connection and will be searched in the cptls cache and a CN (certificate's Canonical Name) might be found. If a CN is found and valid, it will be sent to RAD (Resource ADvisor - internal engine responsible for URL Filtering) and the traffic will be categorized according to it. Otherwise, the traffic is continued to be inspected. When a response (server hello) is coming, it is recognized by PM (Pattern Matcher) matching on one of SSL response signatures internal procedure, the certificate will be extracted and sent to WSTLS process in User mode (in one or more traps). The process will try to resolve the certificate and find its CN. It will return an asynchronic ioctl with response to the kernel with the IP+Port and the CN (if found). If a CN is returned, it will be sent to RAD and will be categorized according to it. Otherwise, the IP address will be sent to RAD and will be categorized according to it. Example: if the certificate's CN is google.com, the categories will be "search engine/portal" Debugging & Troubleshooting Run the following debug on the Security Gateway:
Troubleshooting:
Feature - Safe SearchSafe Search feature in web browsers is designed to screen sites that contain sexually explicit content and remove them from the search results. While no filter is 100% accurate, Safe Search helps to avoid content you may prefer not to see or would rather your children did not stumble across.User can change the settings of Safe Search from the browser for each specific search engine. This feature supports Safe Search in search engines (currently Google, Bing and Yahoo). To enable it, enable the URL Filtering blade. Go to Application & URL Filtering tab -> Advanced -> Engine Settings -> Enable "Enforce Safe Search in search engines" and install Security policy How it works Each search engine has its saved "&meter=value" that is added to the URL when 'Safe search' feature is enabled or disabled. For example, when enabling Safe Search engine in Google, it adds "&safe=active" to the URL. And when disabling it, it adds "&safe=off" to the URL. Debugging & Troubleshooting Run the following debug on the Security Gateway:
Problem: Safe Search feature is not working. Troubleshooting:
Feature - Cached and Translated pages categorizationWith this feature disabled, when a user access the cached pages or Google translated pages, the matched category is ‘Search Engine’ since we drop the query string and send to RAD (Resource ADvisor) the Search Engine domain only.For example, when accessing http://www.ynet.co.il cached page from Google, the URL looks like: http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?ix=seb&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8&q=cache%3Awww.ynet.co.il. The category will be the category of "webcache.googleusercontent.com" (Search Engine). This feature extracts the correct domain from the cached / Google translated URL buffer, sends it to RAD and then gets the exact category of the page. To enable it, enable the URL Filtering blade. Go to Application & URL Filtering tab -> Advanced -> Engine Settings -> Enable "Enforce Safe Search in search engines" and install Security policy How it works The signatures are compiled to one PM (Pattern Matcher) that recognizes URLs that try to access the cached/translated pages. When a URL is coming, the PM matching (built from the relevant signatures of this feature) is executed against it. If there is a match on one of the signatures, it means that it is cached or translated page. According to the signature match offset, the host is extracted and sent to RAD and the client will get the correct category of the page. Debugging & Troubleshooting Run the following debug on the Security Gateway:
Troubleshooting:
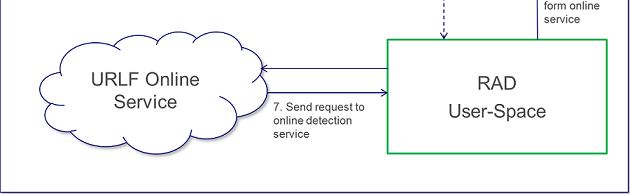
URL Filtering AgentGeneral DescriptionThe new URL Filtering software blade uses a hosted categorization service (cloud-based categorization) that is being constantly updated to cope with the dynamic nature of the web. The Security Gateway is not required to download updates, the categorization database is not limited by the storage space on the Security Gateway, and customers receive the latest categorization to keep policies current.As requests are being sent to the cloud, responses are being cached locally on the Security Gateway so that subsequent requests for the same sites will not query the cloud, but will be answered by the local cache. In deployments of R75.20 URL Filtering, we have seen that more than 99% of requests are being met by the cache, providing customers with the most up-to-date categorization (with the cloud) on the one hand and minimal latency (as most requests are being met by the cache), on the other. When there are critical updates, for example, a previously benign site has been hacked and is now used to spread malware, the cache is invalidated and forced to retrieve updates from the cloud. ProcessesThe R75.20 URL Filtering blade uses a single user mode process called RAD ($FWDIR/bin/rad) to communicate with the online URL Filtering service. The process is initiated once application control, or URL filtering blades, are active on the Security Gateway. Whenever RAD successfully categorizes a URL, it caches it in its kernel cache.The URL Filtering kernel cache holds the entire URL Family (i.e. all the URLs within the same host). Whenever there is a request for a new URL categorization, RAD sends to the online categorization service only the host part of the URL and receives the entire URL family. The response is then cached for future use. Important FilesRAD holds its configuration in 3 files:
URL Filtering Updates and local database (LDB) filesThe RAD kernel cache holds the entire URL Family. Whenever there is a request for a new URL categorization, RAD sends to the online categorization service only the host part of the URL and receives the entire URL family. To keep the response size short, the online service answers only if the URL family has 100 or less members. 99% of the URL database are part of families with 100 or less members and can be retrieved using the online service. The remaining 1% of the database is aggregated in a special file: $FWDIR/appi/update/urlf_db.binThe file is reloaded on each URL Filtering update. Before sending a new online categorization request to the service, RAD looks in the local LDB file for a match. Only if the URL does not exist in the file, a request to the service is made. To trigger a reload of the LDB file: rad_admin urlf update $FWDIR/appi/update/urlf_db.bin Website categorization modeYou can select the mode that is used for web site categorization:
RAD CLI
Main Debug Flags
|
Over three decades of Information Technology experience, specializing in High Performance Networks, Security Architecture, E-Commerce Engineering, Data Center Design, Implementation and Support